What is the Principle of Ion Exchange Resin
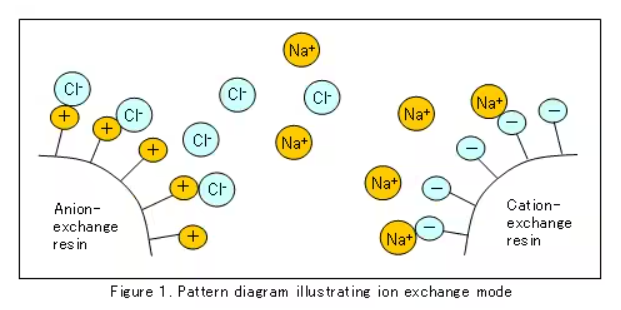
The principles of ion exchange in fact can be summed up in one sentence: the high concentration ions in the solution and the loaded ions on the resin functional groups are exchanged under the promotion of the concentration difference, and the high concentration ions in the final solution hang on the resin. The loaded ions on the ions are displaced into the solution.
We take the 001×7 cation resin which usually used in the softening process of the boiler as an example to show the process situation:
Step1: the sulfonic acid functional groups are full of SO3-H which content H ions. this part of the H ions can freely diffuse and move in a certain range of the aqueous solution. We name it: resin standby state.
Step 2: Add large sum of the NaCL to the solution. Meanwhile, there will be lots of Na ions generated in the solutions. Due to the concentration gap, the high concentration will diffuse to the low concentration part, and the driving force of the concentration difference will push the Na ions to the SO3-H group. Near the cluster, the exchange of Na ions and H ions occurs, and the tube energy cluster changes to SO3-Na. We can call it: resin working state. SO3-H+NCl→SO3-Na+HCl (Note: This reaction is reversible, the middle arrow is bidirectional)
Step 3: continuously replenish NaCl, the exchange process will continue to the right, so that the H on the sulfonic acid group of the resin will become more and more less, on the contrary, the Na ions will become more, and finally all the Na ions will totally be covered. In this way, saturation exchange of the resin is achieved. We can call it: resin exchange (adsorption) saturation state.
From all above, the resin has completed the working process, and the next step is to regenerate the resin.
Step 4: The same principle as the adsorption of Na ions, we add a lot of fresh hydrochloric acid, sulfuric acid, etc. to the solution to ensure a high concentration of H ions in the solution. At this time, the higher concentration of H ions is driven by the concentration difference. , migrated to the vicinity of the functional group covered with Na ions, exchanged with Na ions, the functional group recovered SO3-H, and Na was exchanged into the solution. We can call it: the regeneration process of resin.
SO3-Na+HCl→ SO3-H+NaCl (Note: This reaction is reversible, the middle arrow is bidirectional)
Step 5:Replenish fresh H ions continuously, then the functional group Na of the resin is completely exchanged, and the final functional groups of the resin are all restored to the SO3-H state. We can call it: resin regeneration completed state.
Step 6: Use pure water to rinse the acid solution remaining in the resin pores and crevices. The rinsing end point is generally determined according to the actual use environment. Conductivity, pH value, residual sodium, etc. can be detected. We can call it: the resin rinsing completed state, at this time the resin can be put into the next cycle at any time.
In this way, from the first step to the sixth step, the resin has completed a complete cycle of adsorption and regeneration, and such a cycle is generally called a cycle. Therefore, when we evaluate the life and quality of the resin, in addition to the exchange amount, the rate of infiltrating spheres, and the particle size, the number of cycles is also a very critical indicator.
For the same reason, the exchange principle of anion resin is also to realize the exchange of anions through the effect of concentration difference. For example, the OH supported by the functional group of the anion resin is exchanged with the Cl ions in the solution, and the OH and free H under the exchange are neutralized into water. , the regeneration process is reversed. I won’t go into too much detail here, you can understand it by looking at the content below.
Working process: R-NH2-OH +H+Cl-→ R- NH2-Cl+ H2O
Regeneration process: R-NH2-Cl + NaOH → R-NH2-OH + NaCl
Of course, in the above reaction processes, ions can also be replaced by Ca, Mg, SO4, NO3, etc. The cation resin can exchange Na and Ca ions, and the anion resin can also exchange OH and SO4. Ultimately, it is determined by our use environment. During the delivery process, the priority order of different ions will be discussed in detail later.
Last One :
Next Article :
Related Products
-
 D001macroporous cation ion exchange resinAppearance: Light brown opaque spherical particles.Ionic form:Na+Volume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml): ≥1.80
D001macroporous cation ion exchange resinAppearance: Light brown opaque spherical particles.Ionic form:Na+Volume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml): ≥1.80 -
 201×2 Strong Base Anion Exchange resin(Gel Type)Appearance: Light yellow to gold yellow transparency sphericity particles.The degree of crosslinking : 2%.Ionic form: Cl-
201×2 Strong Base Anion Exchange resin(Gel Type)Appearance: Light yellow to gold yellow transparency sphericity particles.The degree of crosslinking : 2%.Ionic form: Cl- -
 Boron Absorbing Resin Macroporous Ion Exchange Chelating ResinAppearance: Creamy to beige opaque beadsIonic form: Free baseVolume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml): ≥0.80
Boron Absorbing Resin Macroporous Ion Exchange Chelating ResinAppearance: Creamy to beige opaque beadsIonic form: Free baseVolume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml): ≥0.80
Message

