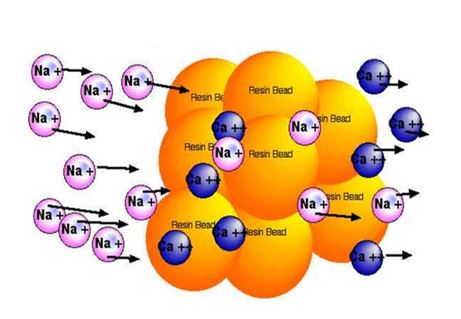
Composition of Ion Exchange Resin
Ion exchange resin is a kind of macromolecular compound with network structure and functional groups. It mainly consists of the following three parts:
(1) Monomer. It is a low-molecular organic substance that can be polymerized into a macromolecular compound. It is the main component of ion exchange resin, so it is also called the matrix. Such as styrene, acrylic acid, etc.
(2) Crosslinking agent. It is a substance that can play a bridging role when linear structure molecules are condensed, so that the groups in its molecules are bonded to each other to form an insoluble network. The commonly used crosslinking agent for ion exchange resin is divinylbenzene. The percentage of crosslinking agent in ion exchange resin is called crosslinking degree. The cross-linking degree of ion exchange resin used in chemical desalination water treatment is generally in the range of 7% to 12%.
(3) Exchange group. It is a group with active ions (exchangeable ions) bonded to the monomer. It can be introduced into the resin by chemical reaction from low molecular weight molecules with dissociation ability [such as sulfuric acid H2SO4, organic amine N(CH)3, etc.]; it can also be directly polymerized by monomers with dissociation groups (such as methacrylic acid).
(1) Monomer. It is a low-molecular organic substance that can be polymerized into a macromolecular compound. It is the main component of ion exchange resin, so it is also called the matrix. Such as styrene, acrylic acid, etc.
(2) Crosslinking agent. It is a substance that can play a bridging role when linear structure molecules are condensed, so that the groups in its molecules are bonded to each other to form an insoluble network. The commonly used crosslinking agent for ion exchange resin is divinylbenzene. The percentage of crosslinking agent in ion exchange resin is called crosslinking degree. The cross-linking degree of ion exchange resin used in chemical desalination water treatment is generally in the range of 7% to 12%.
(3) Exchange group. It is a group with active ions (exchangeable ions) bonded to the monomer. It can be introduced into the resin by chemical reaction from low molecular weight molecules with dissociation ability [such as sulfuric acid H2SO4, organic amine N(CH)3, etc.]; it can also be directly polymerized by monomers with dissociation groups (such as methacrylic acid).

Next Article :
Related Products
-
 Macroporous Weak Acid Chelating Resin for Cobalt Removal Copper Removal Nickel Removal Zinc Removal ResinEquivalent foreign models: Puromet MTS9301Appearance: Spherical BeadsIonic Form: Na+ form
Macroporous Weak Acid Chelating Resin for Cobalt Removal Copper Removal Nickel Removal Zinc Removal ResinEquivalent foreign models: Puromet MTS9301Appearance: Spherical BeadsIonic Form: Na+ form -
 Uranium Extraction Ion Exchange ResinPhysical Form: Opaque beadsIonic form: SulfateTotal Exchange Capacity (Cl− form) mmol/ml: ≥1.30
Uranium Extraction Ion Exchange ResinPhysical Form: Opaque beadsIonic form: SulfateTotal Exchange Capacity (Cl− form) mmol/ml: ≥1.30 -
 DA860 Acrylic Anion Exchange Adsorbent ResinAppearance: Milky white to Light yellow opaque sphericalIonic form:Cl-Volume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml):≥1.6
DA860 Acrylic Anion Exchange Adsorbent ResinAppearance: Milky white to Light yellow opaque sphericalIonic form:Cl-Volume complete exchange capacity(mmol/ml):≥1.6
Message

